Excel or paper-based coordination and documentation of maintenance activities is neither efficient nor process-safe.
The TÜV requirements regarding documentation and archiving can also be met in this way, but only with extremely high effort and a certain susceptibility to errors. The coordination of maintenance activities is based on manual processes and without any automation. In this way, demand-oriented maintenance can only be ensured with considerable effort.
Total Productive Maintenance
- Home
- Total Productive Maintenance
Why is Total Productive Maintenance important for a company?
When coordinating maintenance activities manually and without any sort of digitalization so-called over- or under-maintenance are the consequence. In the case of over-maintenance, maintenance capacities are unnecessarily planned, expensive spare parts and operating materials are consumed, and valuable production time is wasted. Under-maintenance leads to unplanned wear and tear and thus to unplanned production downtimes with time-consuming and expensive ad hoc repair work, which in turn destroys the entire production plan and causes massive costs.
What are the possible solutions for total productive maintenance?
To avoid over- and under-maintenance as well as unplanned machine downtimes, Total Productive Maintenance has been practiced for many years as a key function of the lean management philosophy. Total Productive Management, also known as Total Productive Maintenance, provides a framework for this, based on eight pillars:
- Targeted continuous improvement
- Autonomous maintenance
- Scheduled maintenance
- Competence management
- Quality maintenance
- Start-up management
- TPM in administrative areas
- Occupational safety, health, and environmental protection
Building on these pillars, digitization offers unimagined opportunities to shape and live continuous improvement. Production-related software solutions with machine data acquisition on the controllers enable autonomous maintenance teams to control measures in a targeted manner. The scheduling and execution of measures can be efficiently controlled based on the machine data. At the same time, documentation and analysis take place in the same system without media discontinuity. Legato Sapient offers the tailor-made platform to establish the goals of the TPM philosophy on the store floor.
What is our solution for total productive maintenance?
Legato Sapient creates digital “maintenance cards” in which the measures carried out are documented, archived, and processed in compliance with TÜV. Responsibilities and maintenance intervals are clearly defined. The system automatically calculates due dates based on both time and value using the prescribed, maintenance-relevant criteria. The maintenance team is guided by the interactive dashboards in Legato Sapient and can focus on ensuring a trouble-free and high-performance production process. Operational business is made up of two components, TPM scheduling and TPM orders.
Total productive maintenance tool: Create TPM schedules
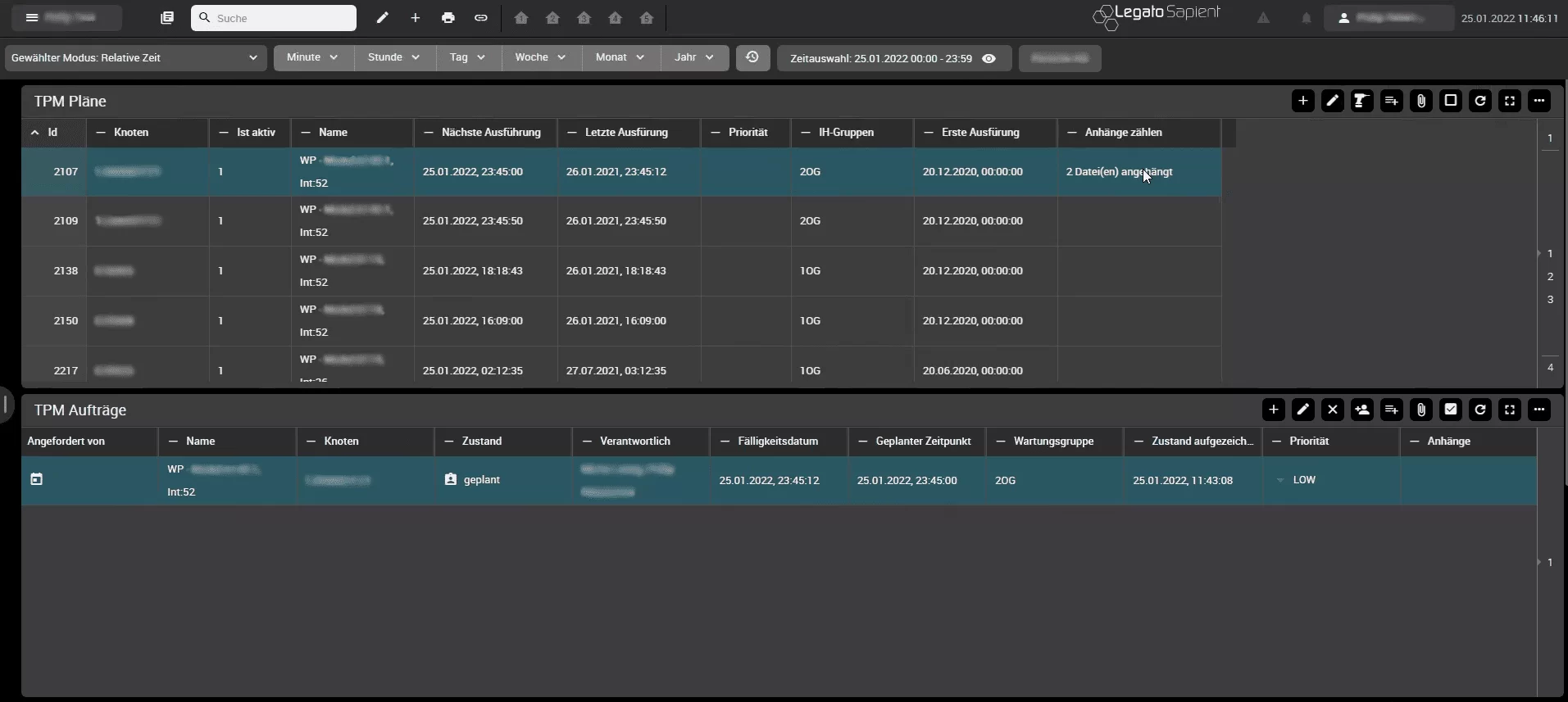
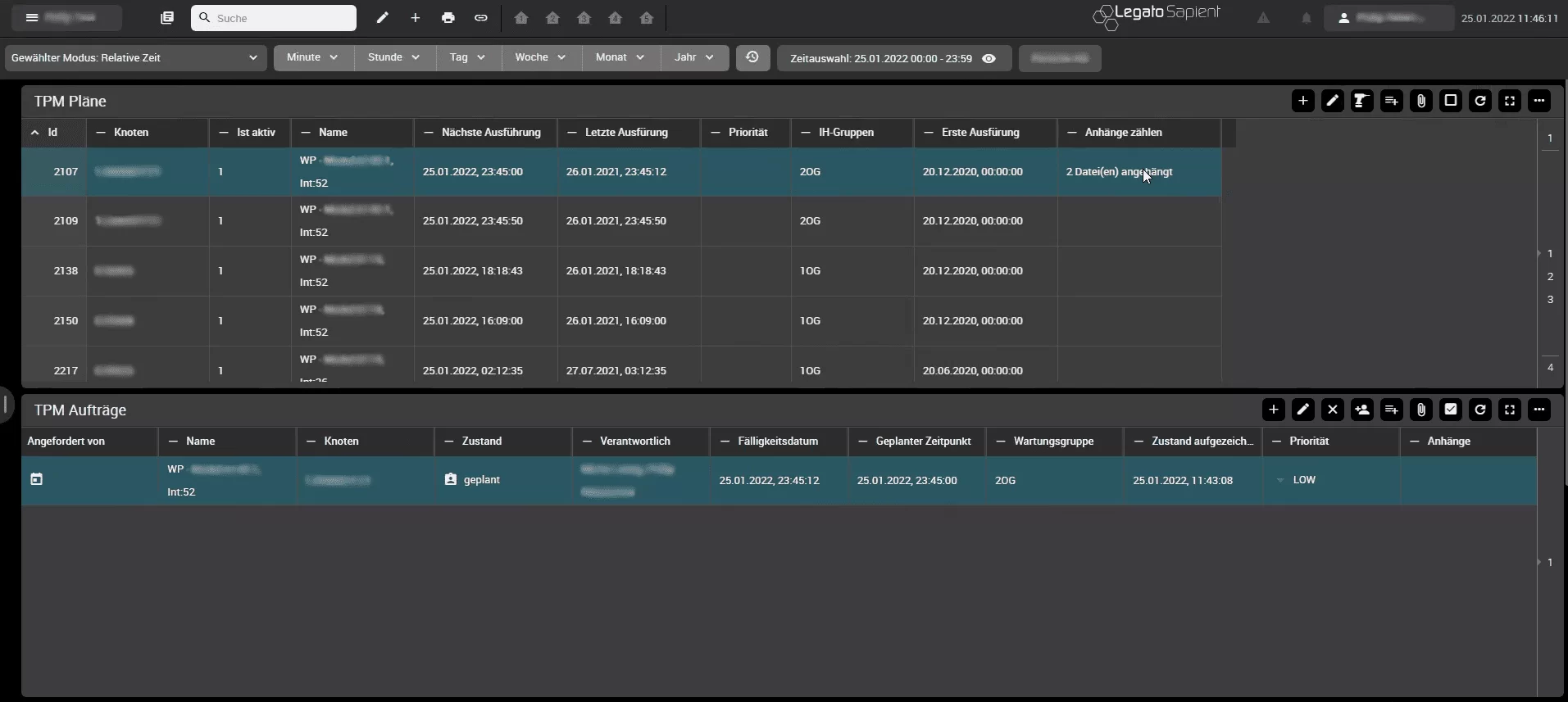
In the TPM Schedule boardlet, maintenance schedules are created and individually assigned to individual plants or machine groups. In this way, an overview of the maintenance schedules of a selected area is created with all maintenance-relevant attributes (ID/name, set time, next due date, last execution, assigned personnel, priority). Furthermore, maintenance plans contain precise descriptions of the work contents and required components.
The visualization shows all available maintenance schedules for the selected (sub-) node in the company structure and is enriched with information such as the next due date, last completion, and the responsible maintenance group. The maintenance schedules can be edited by manually creating new maintenance schedules or by an automated import via csv-files. Furthermore, existing maintenance schedules can be adapted and configured, and files can be attached.
Autonomous maintenance: Create TPM tasks
TPM orders are generated from TPM schedules by means of various triggers. These trigger a maintenance order based on time, value, or message. In addition, it is possible for the plant operator to send a maintenance request on an ad-hoc basis. Time-based Legato Sapient triggers the orders as soon as a defined interval of days or shifts has elapsed. For value-based triggering, online data from the control system is evaluated, which triggers an order when threshold or limit values are reached (e.g., number of pieces produced, throughput or vibration values). Message-based jobs are created by Legato Sapient when the controller sends a dedicated alarm.
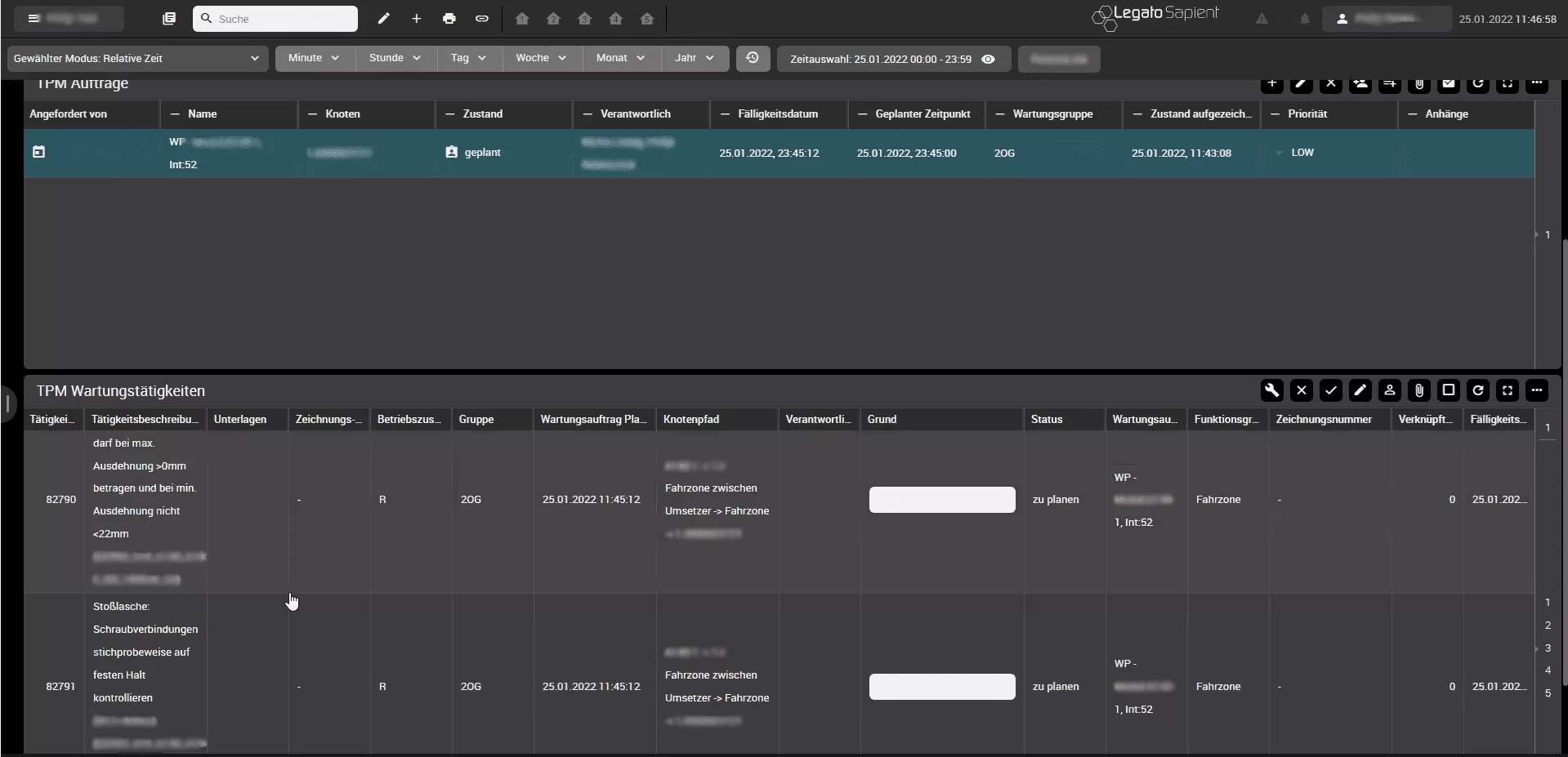
For the preparation of the execution (commissioning, confirmation, etc.) all due maintenance orders are listed in a boardlet. This visualization provides the maintenance team with an overview of all open maintenance orders for the selected (sub-) node. It contains relevant information such as planned due date, the trigger, and the current state/status. The overview of all due maintenance orders enables the maintenance manager to target resources and the maintenance teams to get a list of open tasks. For the structured processing of the maintenance orders and management of the activities, the orders are assigned to one or more persons from the corresponding maintenance group. Legato Sapient provides all relevant information for the processing of the orders. This includes detailed activity descriptions, status, required material or file attachments (e.g., operating instructions and manuals).
Total Production Maintenance analysis
To make the benefits of continuous process optimization advertised at the beginning tangible, Legato Sapient includes an additional module for TPM analysis. This shows the current situation on the store floor at the operational level by means of visualization and monitoring of plant status and alarms as well as the status of maintenance orders. In retrospect, it enables the evaluation and comparison of historical data, especially alarms, maintenance-specific KPIs (MTTR, MTBF, availability, etc.) and maintenance history (tasks, timestamps, responsibility). In this way, performance improvement can be proven, and an active CIP can be established.
Added value for the customer
The described (digitalized) process with the help of Legato Sapient results in added value for you as a customer in many respects:
Replacement of paper- and/or excel-based maintenance activities
- Significant paper reduction on the way to paperless production
- TÜV-compliant – in terms of documentation requirements and archiving
Demand-oriented coordination of maintenance activities to avoid over-maintenance
- Waste of expensive production time
- Waste of maintenance capacities
- Waste of expensive spare parts/operating materials.
Demand-oriented coordination of maintenance activities to avoid under-maintenance
- Avoid unplanned downtimes (due to unplanned failure of a plant) with expensive ad-hoc repairs; better plant availability
- Avoid quality defects in the manufactured products, due to non-removal of chips, missing operating materials or similar
- Safety risks due to faulty safety doors or similar.
The coordination of the due maintenance activities is done by the maintenance manager or the TPM coordinator.
- automatic notification of the relevant groups of people (maintenance manager, TPM coordinator)
- Assigned maintenance tasks appear in a “To-do-list” for the respective maintenance groups.
Transparency in the system
- “Foresight” of future maintenance: Maintenance counters can be viewed in the system at any time
- Central documentation of all performed maintenance activities incl. responsibility and date
- Possible correlations between faults and maintenance intervals can be identified
Click Demo for our Total Productive Maintenance Modul
The following screenshot shows the maintenance schedules available in the system and the maintenance orders due for the selected area (node in the production structure).
In addition, various information, such as next due date, last execution or the responsible maintenance group is displayed – however, the view can be flexibly adapted.
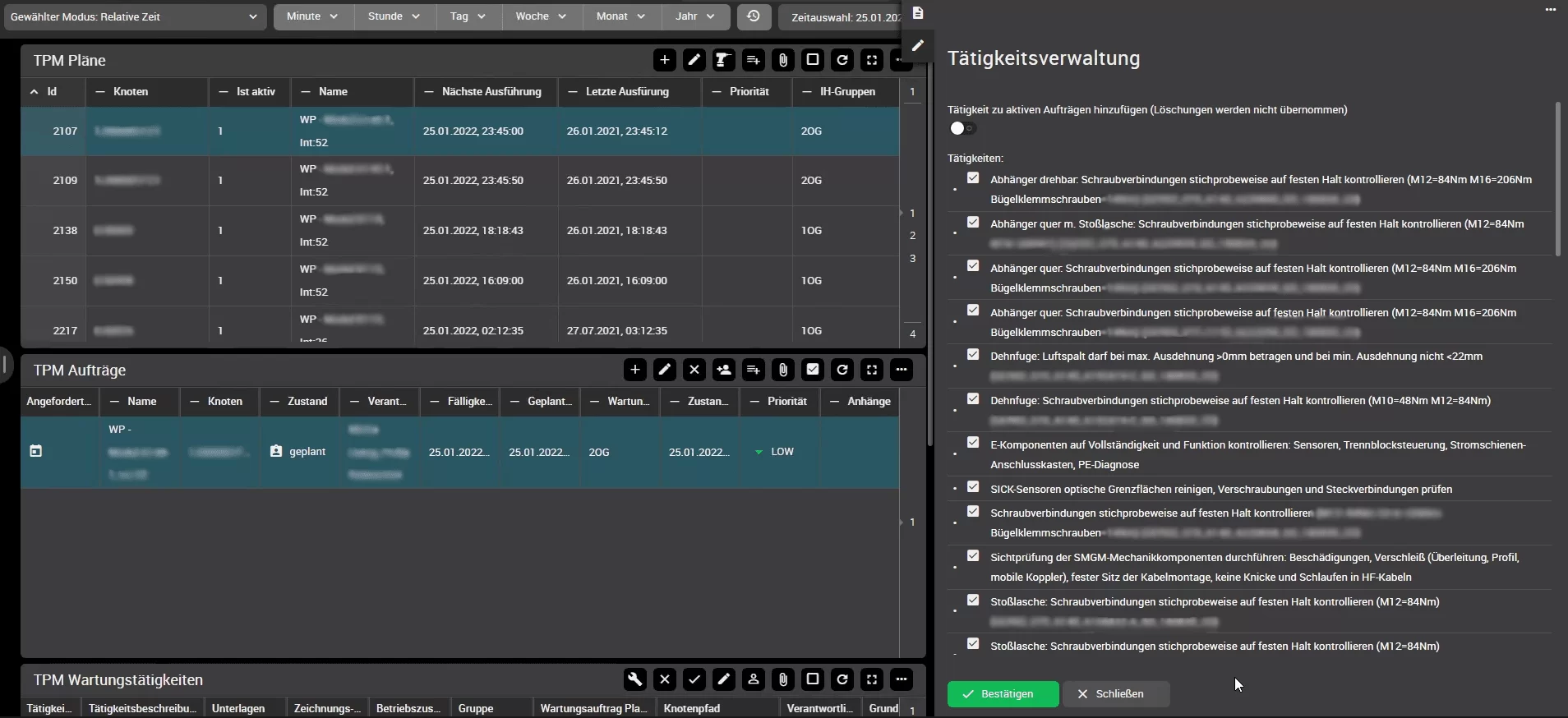
Maintenance schedules can also be edited in this view. For example, existing maintenance schedules can be adapted, or new maintenance schedules can be created. In addition, the system naturally also offers an automated import of maintenance schedules, e.g., via csv files. Via the pencil icon in the upper right corner of the maintenance schedule boardlet, a selected maintenance schedules (see blue-backgrounded line) can be edited. For example, the activities within the maintenance schedule can be edited or adapted:
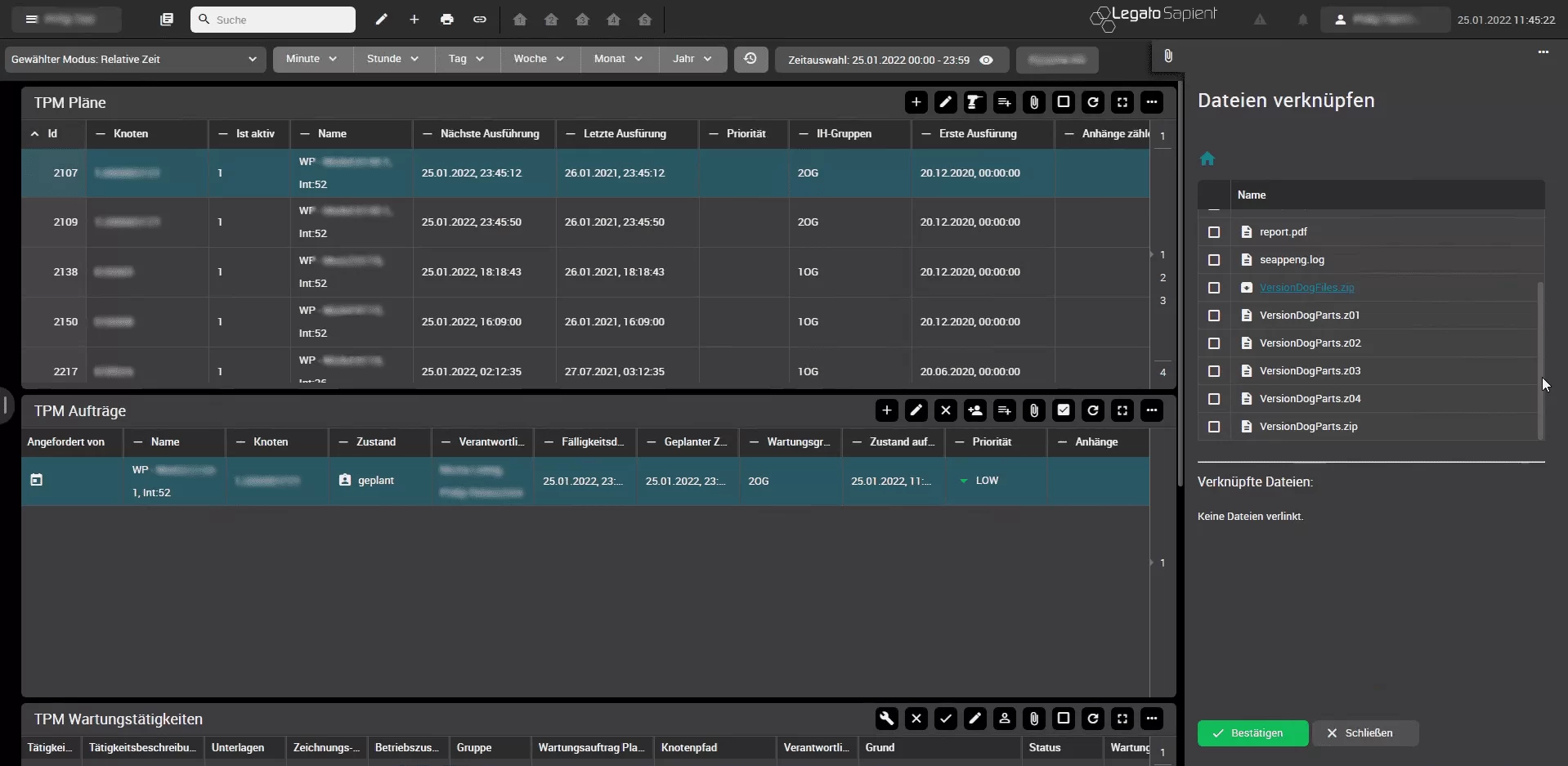
Furthermore, attachments such as technical drawings or similar can be attached as appendices to maintenance schedules:
When a maintenance schedule is selected (see blue-backgrounded line), the triggered, due maintenance order(s) appear in the lower part of the screenshot (maintenance orders are triggered from maintenance schedules, e.g., time- or value-based):
Important additional information on the due maintenance orders is of course also displayed, such as the planned due date, the trigger, and the current status of the maintenance order.
For a maintenance order, one or more persons from the maintenance group can be assigned to the maintenance order.
The following screenshot shows all open maintenance activities of the selected area including the corresponding filter settings. The display of relevant additional information (columns), such as activity description, reason, status, etc. can be flexibly customized.
The activities within a maintenance order are then processed by a responsible person (typically assigned to the maintenance order or activity in advance by the maintenance manager or the TPM coordinator).
Once all the activities of a maintenance order have been completed (including documentation of completion by the maintenance employee), the order is closed, and the corresponding due date counter is reset.
Frequently asked questions about total productive maintenance and autonomous maintenance
Here you will find the most important information on total productive maintenance and autonomous maintenance.
What is total productive maintenance?
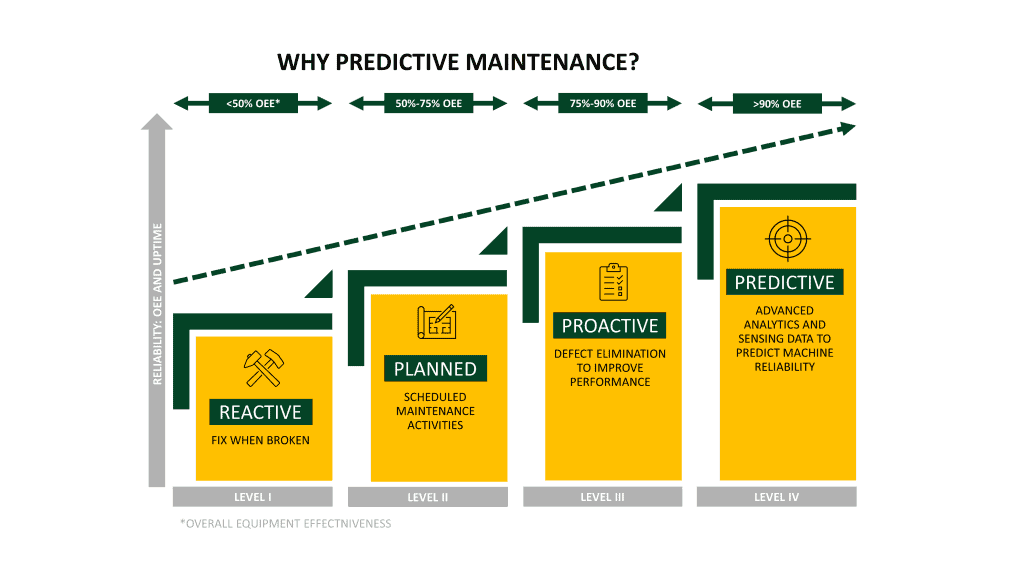
Total productive maintenance means the control of the entire maintenance scheduling on a technical as well as administrative level. This includes the inspection, maintenance, and repair of machines, but also the improvement of work processes. The analytical and strategic approach, for example in determining time intervals for maintenance activities or assigning responsibilities, is essential for holistic maintenance management. The goal of maintenance scheduling is to keep maintenance costs low while increasing overall plant effectiveness (OEE).
What are the strategies in total productive maintenance?
In total productive maintenance, we differentiate between corrective, preventive, and predictive maintenance. In corrective maintenance, machines are not repaired until a failure occurs. Accordingly, there are no costs for maintenance and maintenance scheduling, but failures lead to unplanned downtimes, possibly the machine produces significantly more scrap due to wear, and the life cycle of the machine is significantly reduced.
In prospective or preventive maintenance, maintenance management is based on the manufacturer instructions for every machine or empirical values for MTBF (mean time between failure). This increases the planning reliability for maintenance and the life cycle of the plant can be extended. However, unforeseen downtimes can still occur since maintenance is based on statistics and not on the actual condition of the plant. This can also lead to a machine being serviced more quickly than necessary, thus incurring additional costs for the company.
Predictive maintenance is condition-based and therefore compliant with the actual condition of the plant. The basis for this is provided by real-time data, which is collected using sensors and modern measurement technology, interpreted by an AI (machine learning solution). The more precise a total productive maintenance software is adapted to the plant, the more efficient maintenance scheduling becomes: Wear and tear is detected more quickly, repairs can be scheduled and take place at lower cost, the life cycle of the machine is extended, and costs for personnel and downtime can be saved.
Is predictive total productive maintenance efficient?
With predictive maintenance management, you can significantly optimize maintenance costs and downtime. This gives you an important competitive advantage. In addition, plant maintenance helps to conserve resources because you can use the machines over the long term. The prerequisite is that the maintenance software is precisely tailored to your plant and production.
What does autonomous maintenance mean?
Autonomous maintenance means referring basic maintenance tasks, e.g., cleaning or lubrication, to the machine operator working with the machine on a daily basis. Involving the everyday operator will enhance their understanding of the machine, enabling them to recognize malfunctions early on while technicians are not busy taking care of minor maintenance but can concentrate on the repair tasks.